자바 객체 복사 방법
자바에서는 객체를 복사하는 경우 참조 값으로만 복사가 됩니다. 하지만 상황에 따라 값 자체를 복사해야 하는 경우가 있습니다. 이렇게 자바의 복사 방법은 얕은 복사와 깊은 복사 두 가지 방법이 있습니다.
얕은 복사
얕은 복사(Shallow copy)는 객체를 복사할 때 원본 객체와 복사본 객체가 같은 객체를 참조하는 경우를 말합니다. 즉, 복사본 객체를 수정하는 경우 원본 객체도 변경 사항을 공유하게 됩니다.
public class CopyObjectEx {
private static class Point{
int x,y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point point = new Point(3, 5);
Point[] pointPoll = new Point[1];
pointPoll[0] = point;
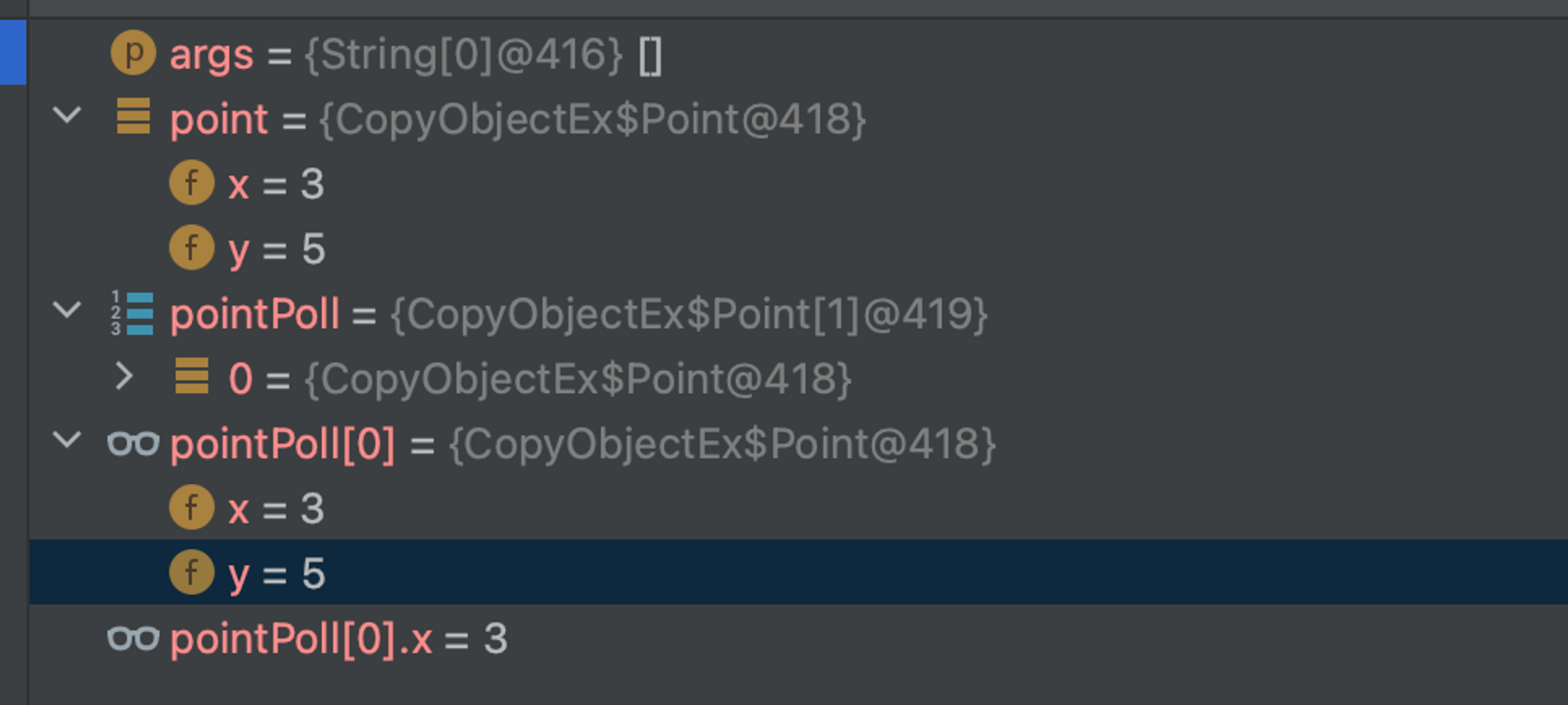
System.out.println(point); // copyObjectEx$Point@5fd0d5ae
System.out.println(pointPoll[0]); //copyObjectEx$Point@5fd0d5ae
point.setX(-1);
System.out.println(pointPoll[0].x); //-1 함께 바뀌는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
}
}위의 코드를 보면 두 포인트가 모두 같은 클래스이름의 해시값을 가진 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
또한 point의 x값만 변경시켰는데 pointPoll내의 x값도 함께 바뀐 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
이는 서로 값은 참조 변수를 가진 경우로 얕은 복사의 경우입니다.
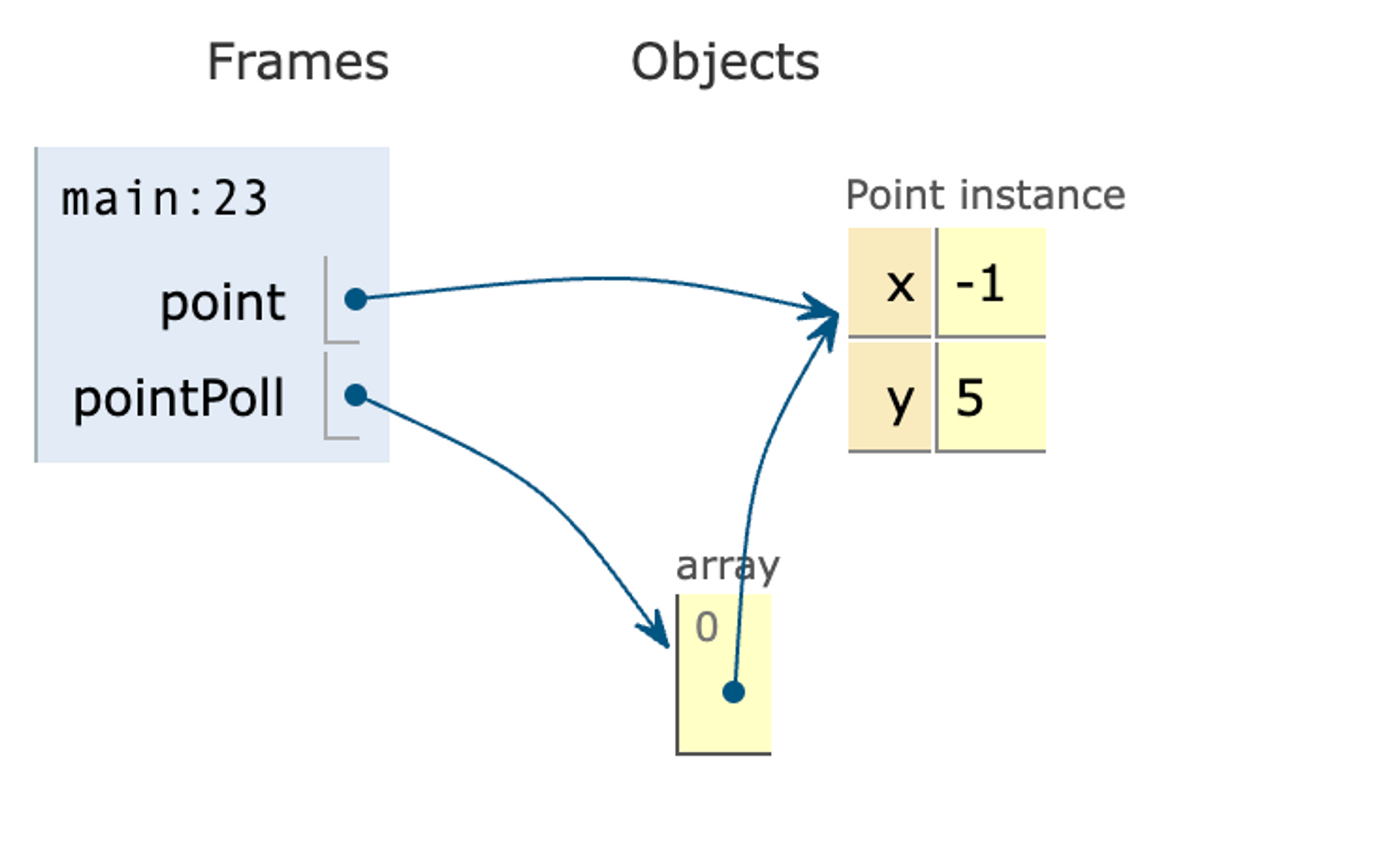
아래 인텔리제이 디버깅을 해보면 point가 서로 같은 위치를 향한다는것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
위의 그림과 같은 상황입니다.
깊은 복사
깊은 복사(Deep copy)는 객체를 복사할 때 원본 객체와 복사본 객체가 서로 다른 객체를 참조하며, 필드 값들도 복사됩니다. 즉, 복사본 객체는 원본 객체와 독립적으로 동작하며, 필드 값의 변경이 서로 영향을 주지 않습니다. 서로 다른 두 객체로 보는 것이 좋습니다.
깊은 복사를 하는 방법에는 여러가지가 있습니다.
1. 생성자, 정적 팩토리 메서드를 이용하는 방식
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CopyObjectEx {
private static class Point{
int x,y;
List<Integer> color = new ArrayList<>();
public Point(int x, int y, List<Integer> color) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.color = color;
}
/** 생성자 이용방식 **/
public Point(Point point) {
this.x = point.x;
this.y = point.y;
// 리스트도 참조형 변수를 가지기 떄문에 깊은 복사의 경우는 새로 인스턴스를 생성해야한다.
// 만약 여기서 단순히 this.color = point.color을 하면
// 두 리스트는 참조변수(가변 변수)로 동일 위치를 가리키기 때문에 얕은복사와 같게 된다.
this.color = new ArrayList<>(this.color);
}
/** 팩토리 메서드 이용방식 **/
public static Point newInstance(Point point) {
return new Point(point);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Point{" +
"x=" + x +
", y=" + y +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Point point = new Point(3, 5, List.of(1, 2));
Point shallowCopy = point;
Point copyPoint = Point.newInstance(point); //복사된 객체
//값
System.out.println(point); //Point{x=3, y=5}
System.out.println(shallowCopy); //Point{x=3, y=5}
System.out.println(copyPoint); //Point{x=3, y=5}
//해시코드(실행 환경마다 값이 다르다)
System.out.println(point.hashCode()); //1595428806
System.out.println(shallowCopy.hashCode()); //1595428806
System.out.println(copyPoint.hashCode()); //1072408673
}
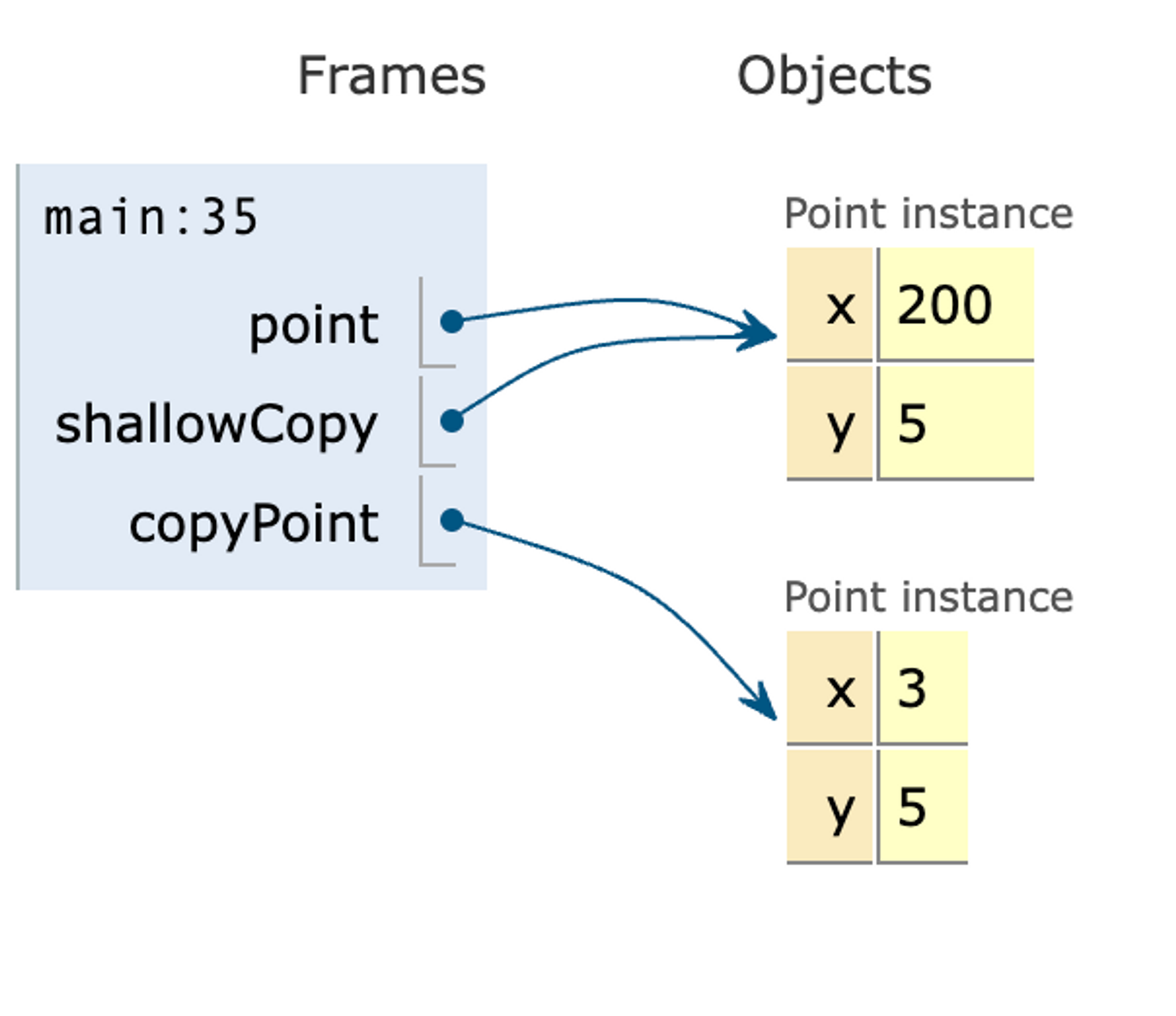
}얕은 복사의 경우는 두 객체의 해시코드(주소값)이 동일 하지만 깊은 복사를 한 경우는 다르다는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
위의 코드는 아래 사진과 같은 경우입니다.
2. clone을 사용하는 경우
1. 객체가 단순 원시형 변수만 가지는 경우
만약 객체가 단순히 원시형변수(primitive)만 가진다면 Clonneable 인터페이스를 이용해서 진행할 수 있습니다.
package com.example.javaprojtectest2.week11.day1;
public class CopyObjectEx2 implements Cloneable {
private static class Point implements Cloneable {
int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
@Override
protected Point clone() {
try {
return (Point)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Point{" +
"x=" + x +
", y=" + y +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point point = new Point(3, 5);
Point shallowCopy = point;
Point copyPoint = point.clone();
point.setX(200);
//값
System.out.println(point); //Point{x=200, y=5}
System.out.println(shallowCopy); //Point{x=200, y=5}
System.out.println(copyPoint); //Point{x=3, y=5}
//해시코드(실행 환경마다 값이 다르다 - 나의 경우)
System.out.println(point.hashCode()); //1595428806
System.out.println(shallowCopy.hashCode()); //1595428806
System.out.println(copyPoint.hashCode()); //1072408673
}
}
2. 내부에 참조형 변수를 가지고 있는 경우
하지만 내부에 참조형 변수를 가지고 있다면 별도로 깊은 복사과정을 추가해주어야 합니다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CopyObjectEx {
private static class Point implements Cloneable{
int x,y;
List<Integer> color = new ArrayList<>();
public Point(int x, int y, List<Integer> color) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.color = color;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
@Override
protected Point clone() {
try {
Point point = super.clone();
point.color = new ArrayList<>(point.color); //가변형 변수의 경우에는 추가해야한다.
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
throw new AssertionError();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Point{" +
"x=" + x +
", y=" + y +
", color=" + color +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point point = new Point(3, 5, new ArrayList<>(List.of(1,2)));
Point shallowCopy = point;
Point copyPoint = point.clone();
point.color.add(200); //추가와 같은 변화에서는 같은걸 사용 만약 새로 할당하면 해당 주소값만 변화.
point.setX(200);
//값 (x의 값 변경시에 포인트의 값만 변경되었고,color에 새로운 값을 추가하면 deepcopy의 경우에는 추가되지 않은것을 확인할 수 있습니다)
System.out.println(point); //Point{x=200, y=5, color=[1, 2, 200]}
System.out.println(shallowCopy); //Point{x=200, y=5, color=[1, 2, 200]}
System.out.println(copyPoint); //Point{x=3, y=5, color=[1, 2]}
//해시코드
System.out.println(point.hashCode()); //1922154895
System.out.println(shallowCopy.hashCode()); //1922154895
System.out.println(copyPoint.hashCode()); //883049899
//color의 주소값이 다르다
System.out.println(point.color.hashCode()); //31014
System.out.println(copyPoint.color.hashCode()); //994
}
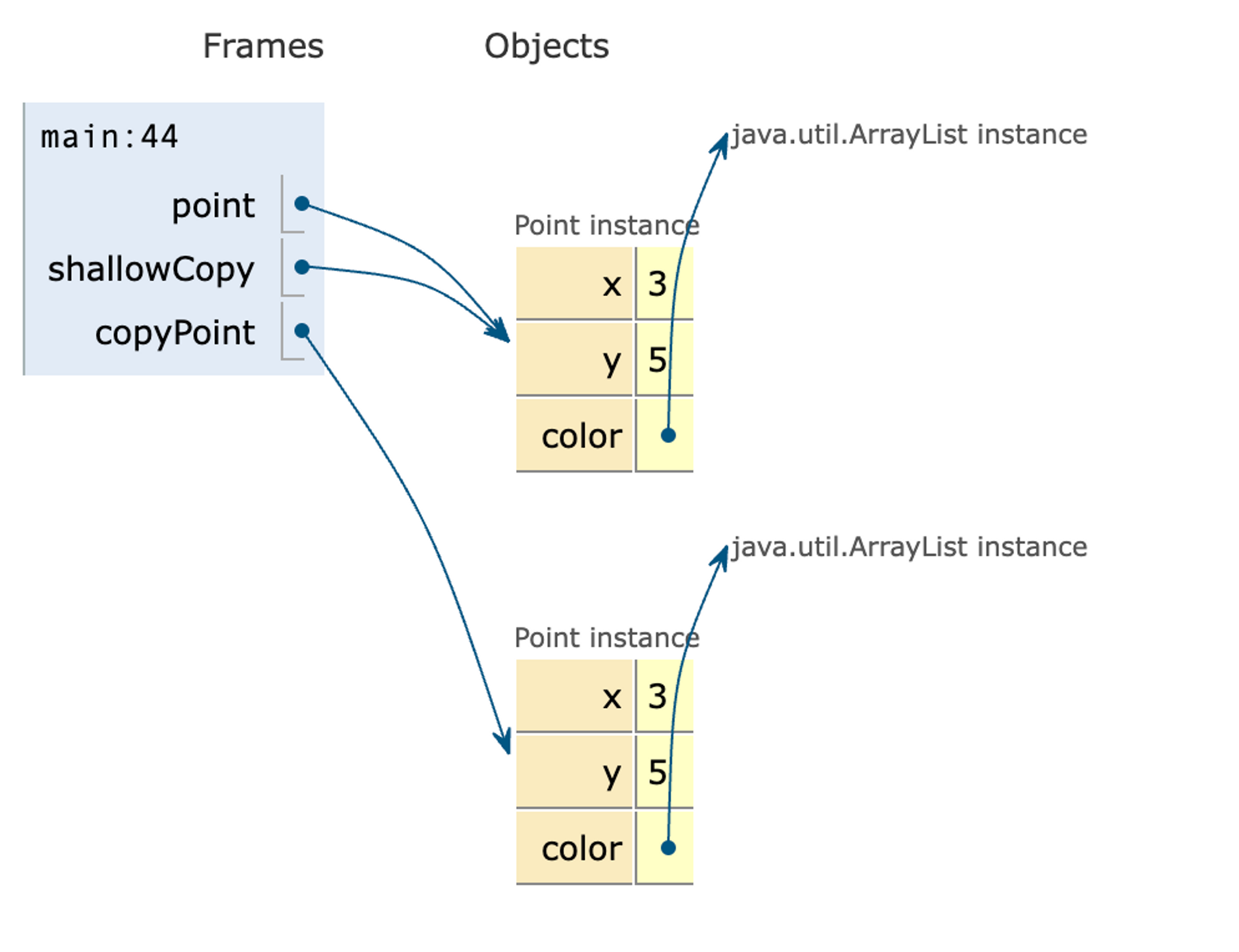
}
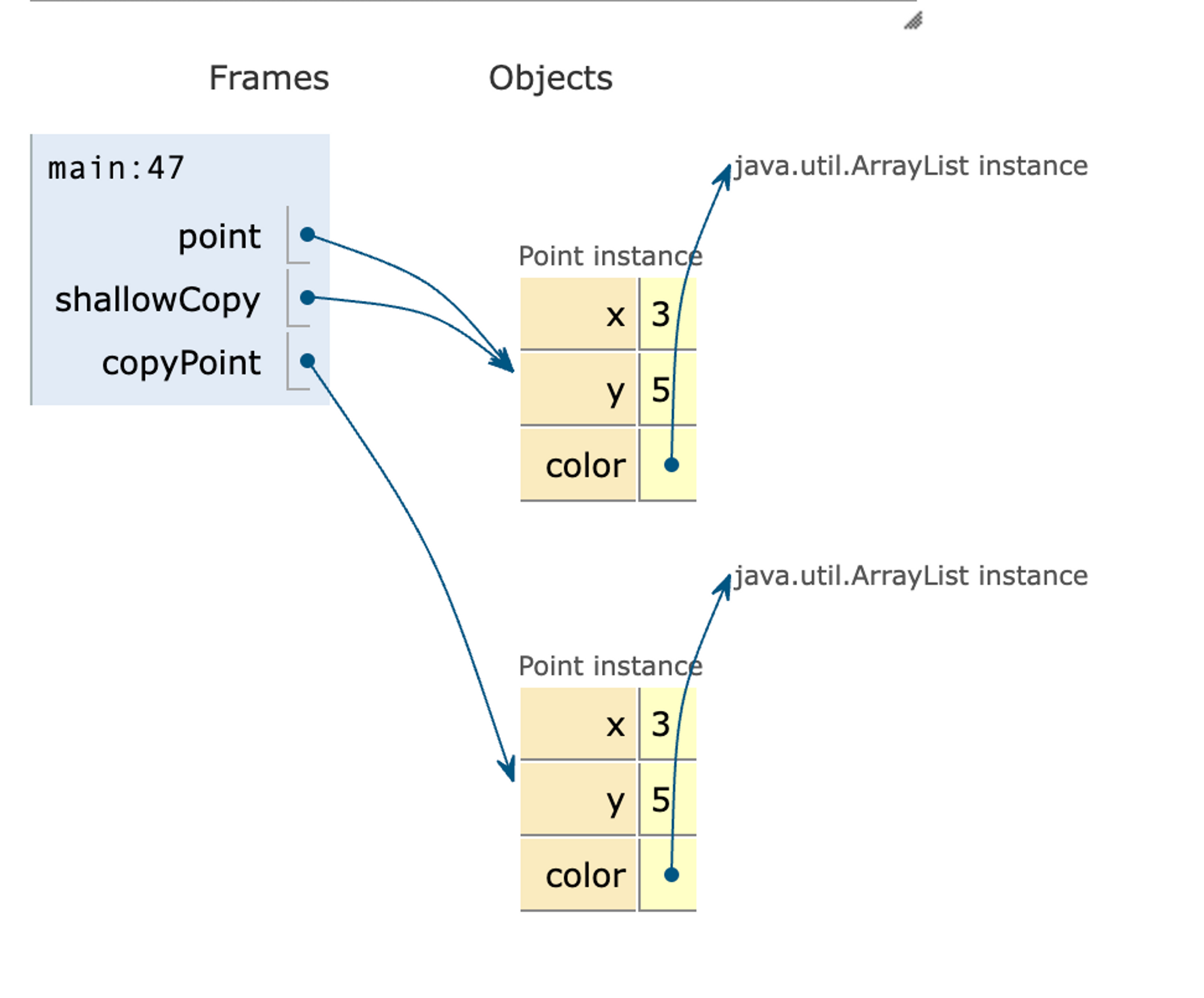
하지만, 만약 참조형 변수를 필드로 가지고 있는데 단순히 클론만 진행한다면 복사된 color의 값과 기본 point의 컬러의 값이 서로 영향을 받는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CopyObjectEx {
private static class Point implements Cloneable{
int x,y;
List<Integer> color = new ArrayList<>();
public Point(int x, int y, List<Integer> color) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.color = color;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
@Override
protected Point clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Point) super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Point{" +
"x=" + x +
", y=" + y +
", color=" + color +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Point point = new Point(3, 5, new ArrayList<>(List.of(1,2)));
Point shallowCopy = point;
Point copyPoint = point.clone();
point.color.add(200); //추가와 같은 변화에서는 같은걸 사용 만약 새로 할당하면 해당 주소값만 변화.
point.setX(200);
//값 color이 서로 영향을 받은것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
System.out.println(point); //Point{x=200, y=5, color=[1, 2, 200]}
System.out.println(shallowCopy); //Point{x=200, y=5, color=[1, 2, 200]}
System.out.println(copyPoint); //Point{x=3, y=5, color=[1, 2, 200]}
//해시코드
System.out.println(point.hashCode()); //1922154895
System.out.println(shallowCopy.hashCode()); //1922154895
System.out.println(copyPoint.hashCode()); //883049899
//color의 주소값이 동일하다.
System.out.println(point.color.hashCode()); //31014
System.out.println(copyPoint.color.hashCode()); //31014
}
}현재 위의 코드는 아래 사진과 같이 가변형 변수가 서로 같은 ArrayList를 가리키고 있다는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
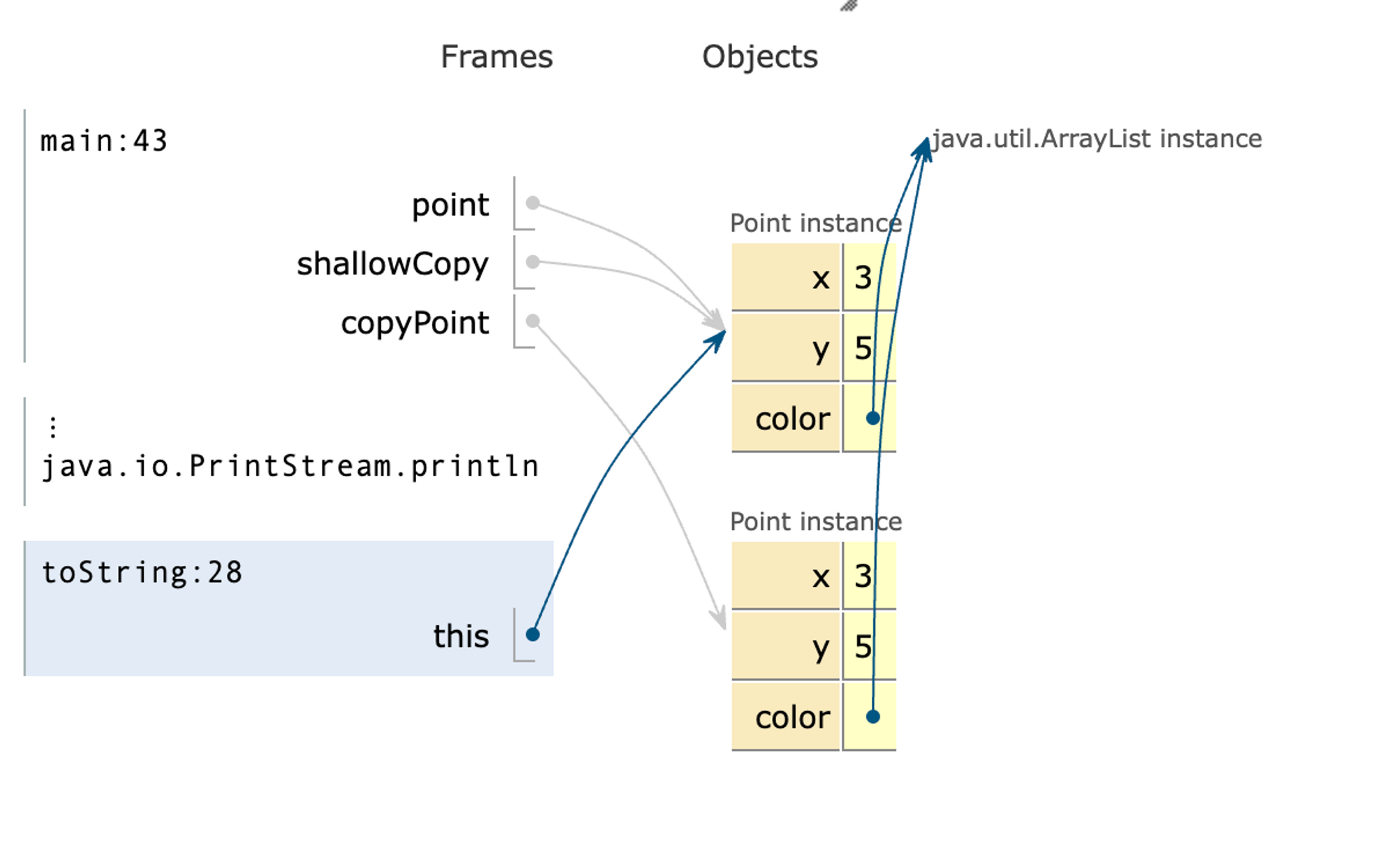
추가로 직렬화, 역 직렬화를 통해 객체를 바이트 코드 변환하고 다시 객체로 쓰는 방법 등이 있습니다.
참고
자바에서 객체의 주소를 출력하는 방법은 아래와 같은 방법이 있습니다.

댓글